当贝市场安卓版

- 文件大小:11.54MB
- 界面语言:简体中文
- 文件类型:Android
- 授权方式:5G系统之家
- 软件类型:装机软件
- 发布时间:2024-10-08
- 运行环境:5G系统之家
- 下载次数:292
- 软件等级:
- 安全检测: 360安全卫士 360杀毒 电脑管家
系统简介
基岩的英文是 "bedrock"。
Introduction to Bedrock
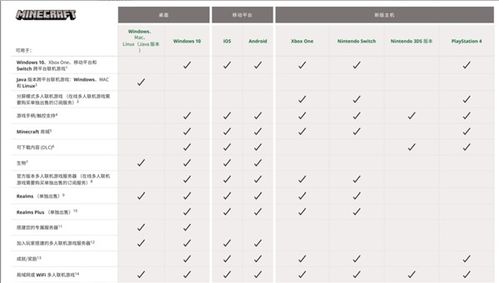
Bedrock, also known as rock bed or foundation rock, plays a crucial role in the geological and structural framework of the Earth. This article delves into the definition, characteristics, formation, and significance of bedrock, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential geological feature.
Definition and Characteristics
Bedrock refers to the solid rock that forms the underlying foundation of the Earth's crust. It is composed of various types of rocks, including granite, gneiss, schist, and limestone. Unlike the soil and sediment that cover it, bedrock is not easily eroded and remains relatively stable over geological timescales.
Characteristics of bedrock include its hardness, durability, and resistance to weathering. These properties make it a stable foundation for buildings, roads, and other infrastructure. Additionally, bedrock often contains valuable minerals and resources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas.
Formation of Bedrock
The formation of bedrock is a complex process that occurs over millions of years. It involves several geological processes, including the following:
Sedimentation: Sediments, such as sand, silt, and clay, accumulate in layers and eventually become compacted and cemented together to form sedimentary rocks.
Metamorphism: Existing rocks are subjected to high temperatures and pressures, causing them to change in mineral composition and texture, forming metamorphic rocks.
Magmatic Activity: Magma, molten rock from the Earth's interior, cools and solidifies to form igneous rocks, which can then become part of the bedrock.
Significance of Bedrock
Bedrock is of great importance for several reasons:
Geological Structure: Bedrock provides the framework for the Earth's geological structure, influencing the formation of mountains, valleys, and other landforms.
Resource Exploration: The presence of valuable minerals and resources in bedrock makes it a target for mining and exploration activities.
Infrastructure Development: Bedrock serves as a stable foundation for buildings, roads, and other infrastructure, ensuring long-term durability and safety.
Environmental Impact: The study of bedrock helps scientists understand the Earth's past and present geological processes, as well as the potential environmental impacts of human activities.
Types of Bedrock

Bedrock can be categorized into three main types based on its origin:
Sedimentary Bedrock: Formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, such as sandstone, shale, and limestone.
Metamorphic Bedrock: Resulting from the transformation of existing rocks under high temperatures and pressures, such as gneiss and schist.
Igneous Bedrock: Composed of cooled and solidified magma, such as granite and basalt.
Conclusion

Bedrock is a fundamental component of the Earth's crust, providing a stable foundation for the planet's surface and supporting a wide range of geological and human activities. Understanding the characteristics, formation, and significance of bedrock is essential for various fields, including geology, engineering, and environmental science.
Tags:
bedrock, rock bed, foundation rock, sedimentary rocks, metamorphic rocks, igneous rocks, geological structure, resource exploration, infrastructure development, environmental impact
常见问题
- 2025-12-13 地狱有什么不好游戏官网版
- 2025-12-13 扫地的十八般武艺
- 2025-12-13 一网畅行
- 2025-12-13 魔秀个性壁纸
装机软件下载排行

其他人正在下载
- 藏家圈藏品平台
- 树术数藏
- 寓小二安卓版
- 二狗单身青年自救平台
- whatsapp官方最新版下载
- imtoken最新版v2.13.5下载
- Letstalk官网版中文下载
- whatsapp官方app
- skype手机官网版下载
- OpenSea钱包最新版
系统教程排行
- 880次 1 oppo用什么安卓系统,引领智能体验新篇章
- 312次 2 oppo用什么安卓系统,引领智能体验新篇章
- 454次 3 怎么升级qq安卓系统,畅享智能体验
- 542次 4 怎么升级qq安卓系统,畅享智能体验
- 507次 5 安卓如何用ios系统,你可以使用其他编程语言或在线工具来实现类似的功能。
- 735次 6 安卓如何用ios系统,你可以使用其他编程语言或在线工具来实现类似的功能。
- 76次 7 电脑安卓系统方形图标,探索安卓方形图标背后的设计奥秘
- 536次 8 电脑安卓系统方形图标,探索安卓方形图标背后的设计奥秘
- 818次 9 安卓系统蓝牙耳机用法,轻松连接与畅享音乐体验
- 890次 10 安卓系统蓝牙耳机用法,轻松连接与畅享音乐体验